Diet Plan for Weight Loss for Females: Healthy & Balanced (Free PDF)
Stop guessing. We analyzed top medical and clinical nutrition guidelines to design a culturally appropriate diet plan that is realistic, flexible, and sustainable.
A healthy weight loss diet for women focuses on balanced nutrition rather than restriction. It includes lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, while supporting hormonal balance, PCOS management, menstrual health, and key nutrients like iron and calcium. Emphasis is placed on portion control, high fiber intake, limited added sugar, and adequate hydration to promote gradual, sustainable weight loss that works in real life.
Core Principles for Weight Loss
Core principles for weight loss are evidence-based rules that consistently produce fat loss while preserving health, muscle mass, and metabolic function.
1. Maintain a Daily Calorie Deficit of 300–500 kcal
Explanation: Fat loss occurs when energy intake is lower than energy expenditure. A deficit of 300–500 kcal/day supports sustainable fat loss (≈0.5–1 kg/week) while minimizing muscle loss, hormonal disruption, and metabolic slowdown. Extreme calorie restriction reduces long-term success.
2. Consume 20–30 g Protein Per Meal to Preserve Muscle
Explanation: Protein intake of 20–30 g per meal (≈1.0–1.2 g/kg/day) reduces hunger, increases satiety, and prevents lean muscle loss during calorie restriction. Muscle preservation maintains metabolic rate and improves weight maintenance.
3. Eat 25–35 g Fiber Daily to Control Appetite
Explanation: Dietary fiber slows digestion, stabilizes blood glucose, and prolongs fullness. Consuming 25–35 g fiber/day from vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains naturally reduces calorie intake without conscious restriction.
4. Include Carbohydrates Daily From Whole-Food Sources
Explanation: Carbohydrates should provide 40–50% of daily calories, primarily from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Eliminating carbohydrates is unnecessary and often impairs energy levels, hormonal balance, and adherence.
5. Limit Added Fats to 2–3 Teaspoons Per Day
Explanation: Dietary fats support hormonal health but are calorie-dense. Limiting fat intake to 2–3 teaspoons of oil per day (≈20–30% of total calories) prevents accidental calorie excess while allowing nutritional adequacy.
6. Control Portion Size Regardless of Food Quality
Explanation: Even nutrient-dense foods contribute calories. Using visual portion control (palm-sized protein, fist-sized carbohydrates, thumb-sized fats) prevents overeating and maintains the calorie deficit without food avoidance.
7. Eat at Regular Intervals Every 3–4 Hours
Explanation: Consistent meal timing improves blood sugar control, reduces hunger spikes, and lowers the risk of binge eating. Skipping meals increases total daily calorie intake in most individuals.
8. Drink 2.5–3.0 Liters of Water Daily
Explanation: Adequate hydration supports digestion, metabolic processes, and appetite regulation. Thirst is commonly misinterpreted as hunger, leading to unnecessary calorie consumption.
9. Limit Ultra-Processed Foods to Less Than 20% of Intake
Explanation: Ultra-processed foods are energy-dense and low in satiety. Keeping them below 20% of total intake improves hunger control and dietary adherence without complete restriction.
10. Perform Strength Training 2–3 Times Per Week
Explanation: Resistance training signals the body to preserve muscle mass during weight loss. Maintaining muscle prevents metabolic decline and reduces the risk of weight regain.
11. Sleep 7–9 Hours to Regulate Hunger Hormones
Explanation: Inadequate sleep increases cortisol and ghrelin while decreasing leptin, making fat loss biologically harder. 7–9 hours of sleep is a non-negotiable component of weight loss.
12. Prioritize Consistency Over Perfection (80% Rule)
Explanation: Adherence over 6–12 months determines success. Following the plan 80% of the time produces better long-term outcomes than short-term strictness.
Diet Plan for Weight Loss for Females
| Time | Meal | Option | Diet Item | Exact Quantity / Preparation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6:30–7:00 AM | Pre-Breakfast | Option 1 | Apple Cider Vinegar Water | 1 tsp ACV in 1 glass room-temperature water (use on alternate days in a week) |
| Option 2 | Zeera Water | Soak 1 tsp zeera in 1 glass water overnight, strain and drink in the morning | ||
| Option 3 | Lemon–Chia Water | Juice of ½ lemon + soaked chia seeds in 1 glass lukewarm water | ||
| 7:30–8:30 AM | Breakfast | Option 1 | Bran bread + omelette + tea | 1 bran bread + omelette (2 egg whites + ¼ cup optional vegetables) cooked in 1 tsp oil + 1 cup tea (no white sugar) |
| Option 2 | Yogurt + chia + egg whites | 1 cup fat-free yogurt (no sugar) + 1 tsp soaked chia seeds + 2 boiled egg whites | ||
| Option 3 | Eggs + milk | 3 boiled egg whites (no yolk) + 1 cup milk (without sugar) | ||
| 10:30–11:00 AM | Brunch | Option 1 | Apple | 1 small apple |
| Option 2 | Orange | 1 medium orange | ||
| Option 3 | Banana | 1 small banana | ||
| 1:00–2:00 PM | Lunch | Option 1 | Salad + chickpeas | 1 cup mixed salad (80 g) + 1.5 tbsp boiled chickpeas (olive oil optional; black pepper, salt, vinegar allowed) |
| Option 2 | Salad + chicken | 1 cup mixed salad (80 g) + 5 small grilled/boiled chicken boti (shredded) | ||
| Option 3 | Daal + rice + salad (once/week) | ½ cup cooked daal (100 g) + ½ cup cooked rice (100 g) + ½ cup mixed salad (40 g) | ||
| 4:30–5:00 PM | Snack Time | Option 1 | Black coffee + almonds | 1 cup black coffee + 7 almonds |
| Option 2 | Black coffee + popcorn | 1 cup black coffee + ½ cup popcorn | ||
| 7:00–8:00 PM | Dinner | Option 1 | Chapatti + homemade dish | 1 small whole-wheat chapatti (40 g) + any homemade dish + ¼ cup salad |
| Option 2 | Chapatti + BBQ chicken | 1 small chapatti (40 g) + 90–100 g cooked BBQ chicken (2 medium boti) + ¼ cup salad | ||
| Option 3 | Chapatti + fish | 1 chapatti + 100 g coal-cooked or steamed fish (no skin, 1 medium fillet) + ¼ cup salad |
Recommendations for Healthy Weight Loss
Hydration
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Drink 1 glass of water 30 minutes before each meal.
- Avoid drinking water immediately after meals.
- Sip water regularly, approximately every 30 minutes.
Meal Timing and Portions
- Follow fixed meal timings every day.
- Stick strictly to the given portions; avoid extra servings.
- Do not skip meals to accelerate weight loss.
- Eat dinner at least 3 hours before bedtime.
- Avoid heavy or solid foods after dinner.
Food Choices
- Prefer home-cooked meals with minimal oil, salt, and added sugar.
- Avoid junk food, confectionery, carbonated drinks, and highly processed foods.
For snacking:
- Eat a handful of air-popped popcorn, if desired.
- Eat half a fist of nuts (8–10 unpackaged) once per day, if desired.
Supplementation
- Take Calcium D supplement (2 tablets daily) for healthy bones and joints.
- Do not take supplements on an empty stomach unless advised by a doctor.
- Drink ½ cup sugar-free skim milk 30 minutes before bedtime.
Physical Activity
- Do a 45-minute walk before bedtime, ideally in the evening or early night.
- Ensure walking is done at least 1 hour after dinner.
Lifestyle and Mindset
- Weight loss should be gradual and sustainable.
- Your body has a right to care—take steps to stay fit and healthy consistently.
- This plan is not recommended during pregnancy or lactation unless supervised by a doctor.
What to Eat & What to Avoid for Weight Loss
🟢 Green List – Eat Freely
These foods are low in calories, nutrient-dense, and can be consumed without strict portion control.
-
Vegetables (Sabzi): Spinach (Palak), Bottle Gourd (Lauki), Apple Gourd (Tinda), Cucumber (Kheera), Okra (Bhindi), Bitter Gourd (Karela).
Tip: Fill half your plate with these vegetables at every meal. -
Lean Protein: Egg whites, Skinless Chicken Breast, Steamed White Fish (Rahu/Singhara), Low-Fat Homemade Paneer, Lentils (Moong Dal, Masoor Dal), Boiled Chickpeas (White/Black Chana).
Tip: Include a protein source in every meal to maintain satiety and muscle mass. -
Complex Carbohydrates: Whole Wheat Roti (Chakki Atta), Brown Rice, Barley (Jau), Oats (Daliya), Multigrain Bread (check label).
Tip: Prefer whole grains over refined carbs to control blood sugar and prolong fullness. -
Fruits (High Sugar – Limited): Mango (1 slice max), Grapes (small bowl), Banana (1 small), Chikoo.
Tip: Consume as part of a meal rather than standalone snacks to avoid sugar spikes. -
Healthy Fats: Desi Ghee (max 1 tsp/day), Mustard Oil, Olive Oil, Walnuts (2 whole), Almonds (6–7 pieces).
Tip: Include fats in moderation; they support hormones and satiety.
🟡 Yellow List – Portion Control
These foods are nutritious but calorie-dense or high in sugar; consume mindfully.
- Dried fruits and nuts beyond the recommended portions
- Fruits high in sugar if eaten outside meals
- Oils or ghee beyond recommended limit
- Multigrain breads with added sugar – check labels carefully
Tip: Use visual portion control: palm-sized protein, fist-sized carbs, thumb-sized fats.
🔴 Red List – Avoid or Swap
These foods are high in refined carbs, sugar, or unhealthy fats and hinder weight loss.
- Refined Carbs & Bakery Items: Maida products: Pizza, Burgers, Naan (Roghni/White), White Bread, Cake Rusk, Biscuits, Pasta
- Fried Foods & Snacks: Samosas, Pakoras, Parathas (Deep Fried), Chips, Nimco
- Sugary Foods & Drinks: Jalebi, Gulab Jamun, Cold Drinks, Sodas, Boxed Juices, Sweetened Tea/Coffee, Energy Drinks
Smart Kitchen Swaps
| Avoid | Swap With |
|---|---|
| Creamy Sauces | Tomato-based or Yogurt-based sauces |
| Deep Frying | Air Frying or Steaming |
| Milk Chocolate | 70% Dark Chocolate |
| White Sugar | Stevia, Monk Fruit, or Cinnamon |
Tips for Fast and Healthy Weight Loss
Achieving fast weight loss doesn’t mean extreme diets or starvation. By combining a structured diet with healthy lifestyle habits, you can lose weight efficiently while preserving energy, muscle mass, and overall health.
Aim for 5–6 small meals a day instead of 2–3 large ones.
Helps control hunger, prevent bloating, and stabilize blood sugar.
Include healthy snacks like fruits, nuts, or air-popped popcorn instead of junk food.
Finish your last meal by 8 PM to allow proper digestion.
Avoid heavy foods or late-night eating, which can slow metabolism and increase fat storage.
Drink 6–8 glasses of water daily; water helps curb appetite and boosts metabolism.
Drink a glass of water 30 minutes before meals to prevent overeating.
Include hydrating drinks like lemon water, herbal teas, or infused water (avoid sugar).
Aim for 15–30 grams of fiber per day from oats, lentils, fruits, vegetables, flax seeds, and broccoli.
Fiber promotes satiety, improves digestion, and supports heart health.
Include fiber in every meal to naturally reduce calorie intake.
Include protein in every meal: egg whites, chicken, fish, paneer, or lentils.
Protein preserves muscle mass, increases satiety, and boosts calorie burn via diet-induced thermogenesis.
No screens while eating; focus on your food.
Chew slowly: it takes ~20 minutes for your brain to register fullness.
Portion control: when eating out, save half your meal for later or share.
Cardio: 150 minutes per week (walking, swimming, cycling).
Strength training: 2–3 days/week; muscles burn more calories at rest than fat.
Include non-exercise movement: take stairs, walk short distances, or stand frequently.
Get 7–9 hours of quality sleep nightly.
Chronic stress increases cortisol, which promotes belly fat storage.
Include stress-relief practices: meditation, light yoga, deep breathing, or a short evening walk.
Follow the MIND Diet approach: focus on brain-healthy foods like berries, leafy greens, and nuts to prevent inflammation and brain fog.
Avoid skipping meals to lose weight faster—gradual weight loss is sustainable.
Limit alcohol and sugary drinks; they add empty calories and hinder fat loss.
Drink water before every meal.
Fill half your plate with vegetables.
Include lean protein and complex carbs at every meal.
Limit refined carbs, fried foods, and added sugar.
Walk 45 minutes daily, preferably after dinner.
Track progress weekly, not daily, to stay consistent.
Diet Plan Adjustments for Females With PCOS, Post-Partum Needs, and Menopause
A 25-year-old woman requires a very different nutritional strategy than a 55 year old. This diet plan adapts to key female life stages to ensure it remains practical, evidence based, and effective.
Primary goal: Reduce insulin spikes and improve hormonal balance.
Key adjustments:
- Eat breakfast within one hour of waking to support insulin sensitivity.
- Avoid “naked carbs.” Always pair carbohydrates such as fruit with protein or healthy fats, for example fruit with nuts or yogurt.
- Include insulin supporting foods such as beans and consider spearmint tea as part of the routine.
Primary goal: Support healing, energy levels, and nutrient replenishment.
Key adjustments:
- If breastfeeding, calorie intake should not fall below approximately 1,800 kcal per day.
- Prioritize hydration and iron rich foods such as spinach, lean meat, and traditional yakhni to support recovery.
- Sleep whenever the baby sleeps to aid physical and hormonal restoration.
Primary goal: Preserve muscle mass and protect bone density as estrogen levels decline.
Key adjustments:
- Increase protein intake to approximately 30 grams per meal to reduce muscle loss.
- Focus on calcium and vitamin D rich foods to support bone health.
- Prioritize strength training over excessive cardio to maintain muscle and skeletal strength.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I lose 10 kg in 7 days?
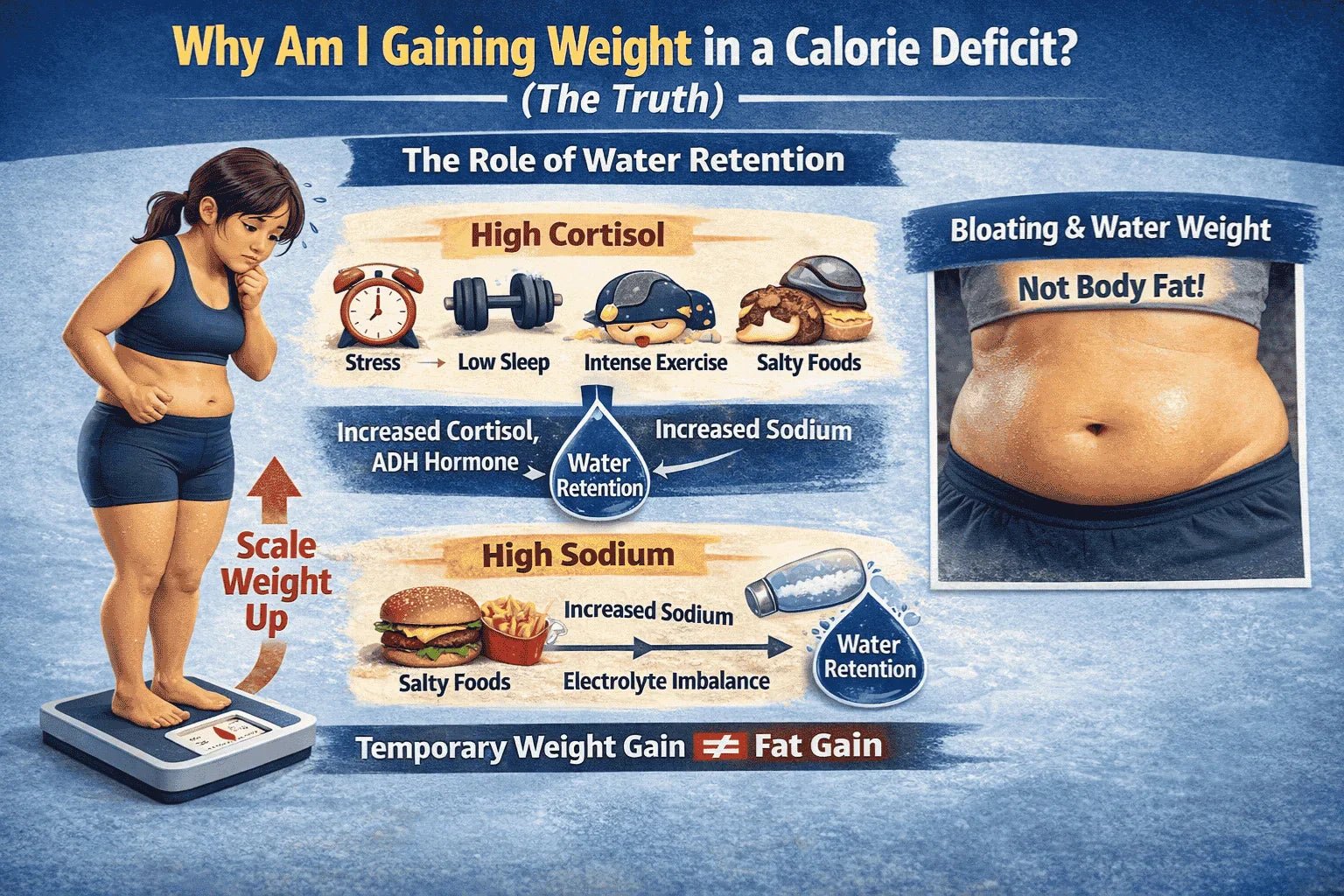
No. Rapid weight loss claims are misleading and unsafe. Most of the weight lost through crash diets is water and muscle, not fat. This approach increases the risk of hormonal imbalance, hair loss, fatigue, and rebound weight gain. According to NHS guidelines, a safe and sustainable rate of weight loss is 0.5 to 1 kg per week.
How much weight can I realistically lose in one month?
A realistic and healthy target is 2 to 4 kg per month, depending on your starting weight, metabolism, and consistency. Slower weight loss is more sustainable and helps preserve muscle mass and hormonal balance.
Is the Keto diet safe for women?
Keto can cause quick weight loss initially, but long term use may negatively affect female hormones, especially thyroid and adrenal function. Many women experience missed periods, fatigue, or mood changes. A balanced, moderate carbohydrate diet is generally safer and more sustainable, particularly for women with PCOS or irregular cycles.
Can women with PCOS lose weight?
Yes. Weight loss with PCOS is possible but requires a different approach. Controlling insulin spikes, avoiding refined carbohydrates, eating regular meals, and pairing carbs with protein or fat significantly improves results. Consistency matters more than extreme restriction.
Can I drink chai or tea and still lose weight?
Yes. The problem is not tea, but added sugar and full fat milk. Use skim or low fat milk, avoid sugar, and use calorie free sweeteners such as stevia if needed. Limit intake to two cups per day for best results.
Can I drink coffee on this diet?
Yes, coffee is allowed. Avoid sugar, flavored syrups, and creamers. Black coffee or coffee with a small amount of low fat milk is preferred. Excess caffeine should be avoided if you have anxiety or sleep issues.
Do I have to stop eating rice to lose weight?
No. Rice can be included in controlled portions. The key is portion size, meal timing, and pairing rice with protein and fiber. Completely eliminating cultural staple foods often leads to poor adherence and rebound weight gain.
How do I control portions without a weighing scale?
Use your hand as a portion guide:
- Palm equals one portion of protein
- Fist equals one portion of vegetables
- Cupped hand equals one portion of carbohydrates such as rice or dal
- Thumb equals one portion of fats such as oil or butter
This method is practical and effective for daily use.
How many meals should I eat in a day?
Most women do well with three main meals and one to two light snacks. Skipping meals can increase cravings, slow metabolism, and worsen hormonal imbalance, especially in women.
Is intermittent fasting safe for women?
Intermittent fasting may work for some women but can disrupt hormones if done aggressively. Women with PCOS, thyroid issues, or irregular periods should follow a gentle, structured eating pattern rather than long fasting windows.
What if I feel hungry on a calorie deficit?
Hunger often means meals are lacking protein, fiber, or healthy fats. Adjust food quality before reducing calories further. Drinking water and ensuring adequate sleep also helps regulate appetite hormones.
Can I exercise while following this diet?
Yes, exercise is encouraged. Strength training is especially important for women to preserve muscle mass and bone density. Cardio can be added in moderation. Excessive cardio without proper nutrition can be counterproductive.
Is this diet suitable after pregnancy?
Yes, with adjustments. If breastfeeding, calorie intake should not drop below 1,800 kcal per day. Hydration, iron intake, and adequate rest are essential for recovery and milk production.
Will this diet affect my menstrual cycle?
A properly designed, balanced diet supports menstrual health. Extreme calorie restriction or very low carbohydrate intake may disrupt periods. This plan prioritizes hormonal balance and nutrient adequacy.
Do I need supplements while following this plan?
Not always. Most nutrients should come from food. However, iron, vitamin D, calcium, or B12 supplementation may be needed depending on individual deficiencies. Always consult a qualified professional before starting supplements.
How long should I follow this diet?
This is not a crash diet. It is designed as a long term lifestyle approach. You can follow it continuously with minor adjustments based on life stage, activity level, and health goals.
What if I stop losing weight?
Weight plateaus are normal. Review portion sizes, activity levels, sleep, and stress. Sometimes increasing protein or strength training helps restart progress without cutting calories further.
We rely on peer-reviewed studies and reputable medical journals.